Consultation
+370 645 64564
info@bauto.lt
Orders
+370 645 64564
uzsakymai@bauto.lt
Consultation
+370 645 64564
info@bauto.lt
Orders
+370 645 64564
uzsakymai@bauto.lt

The OEM code is a unique combination of numbers and letters found on the original part. This code guarantees that the part is made according to all the requirements of the car manufacturer, is of high quality and durable. Here you can find the following engine parts by OEM code.

The engine is a crucial component of a car, as the entire performance of the vehicle depends on it. This mechanism converts received energy into mechanical work, allowing the car to move. The value of a car is largely determined by its engine, so if the engine is in poor condition or requires repair, it will be difficult to enjoy the car.
There can be numerous reasons for engine failure, such as poor oil, a faulty air intake filter, or malfunctioning fuel injectors. However, the most common and costly engine failures occur due to:
To ensure your car's engine stays in optimal condition, it is important to address these issues promptly. At our store, we offer a wide range of original engine parts and accessories to help you maintain and repair your engine efficiently. From high-quality oils and filters to fuel injectors, we have everything you need to keep your engine running smoothly.

Experiencing engine knocking? Most likely, it's the result of detonation. Detonation is an improper fuel combustion caused by an excess of heat and pressure in the combustion chamber of a vehicle. Engine knocking occurs when the fuel mixture ignites too early, and the released energy is primarily used to increase piston friction.
Detonation can also occur due to the use of lower-octane and/or cetane fuel than recommended by the manufacturer. For example, using AI-80 fuel instead of AI-92 for a gasoline engine.
Prolonged engine knocking can damage piston rings, harm the piston itself, and cause cylinder head gasket failure.
To prevent engine knocking and maintain optimal performance, it is crucial to use the recommended fuel with the correct octane or cetane rating. At our store, we provide a wide selection of original engine parts and accessories to help you address and resolve any engine issues effectively.

Oil is essential for engine lubrication. It reduces friction within the engine, thereby lowering its temperature. When the engine is properly lubricated, it operates efficiently and allows for better fuel efficiency. Changing the oil according to the manufacturer's recommendations or even more frequently will definitely not hurt. It is also crucial to use the right and high-quality oil for your vehicle. If the oil is not changed in a timely manner, it accumulates impurities that the filter can no longer remove, leading to damage to the turbocharger. Additionally, the oil thickens over time, making the engine not only harder to start but also consume more fuel.
For optimal engine performance and longevity, it is important to maintain a regular oil change schedule and use the recommended oil grade and type. At our store, we offer a wide range of original and high-quality oils suitable for your vehicle's needs. Visit us today to find the right oil for your engine and ensure its smooth operation.
Remember, taking care of your engine's lubrication is vital for its overall health and performance.

Engine coolant, also known as antifreeze, is crucial for maintaining optimal engine temperature. This fluid removes excess heat from the engine. Additionally, engine coolant protects against rusting of metal components and corrosion of plastic or rubber parts. Without proper coolant, the engine can overheat during internal combustion, leading to engine seizure. It is important to use the coolant recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.
To enjoy your car for a long time without any worries, it is essential to perform regular preventive maintenance procedures on the engine. Neglecting engine maintenance will likely result in the need for costly repairs or even a new engine.
At our store, we provide a wide range of original engine parts and accessories, including engine coolant, to help you maintain your engine's health and performance. Visit us today to find the right coolant for your vehicle and ensure trouble-free driving for years to come.
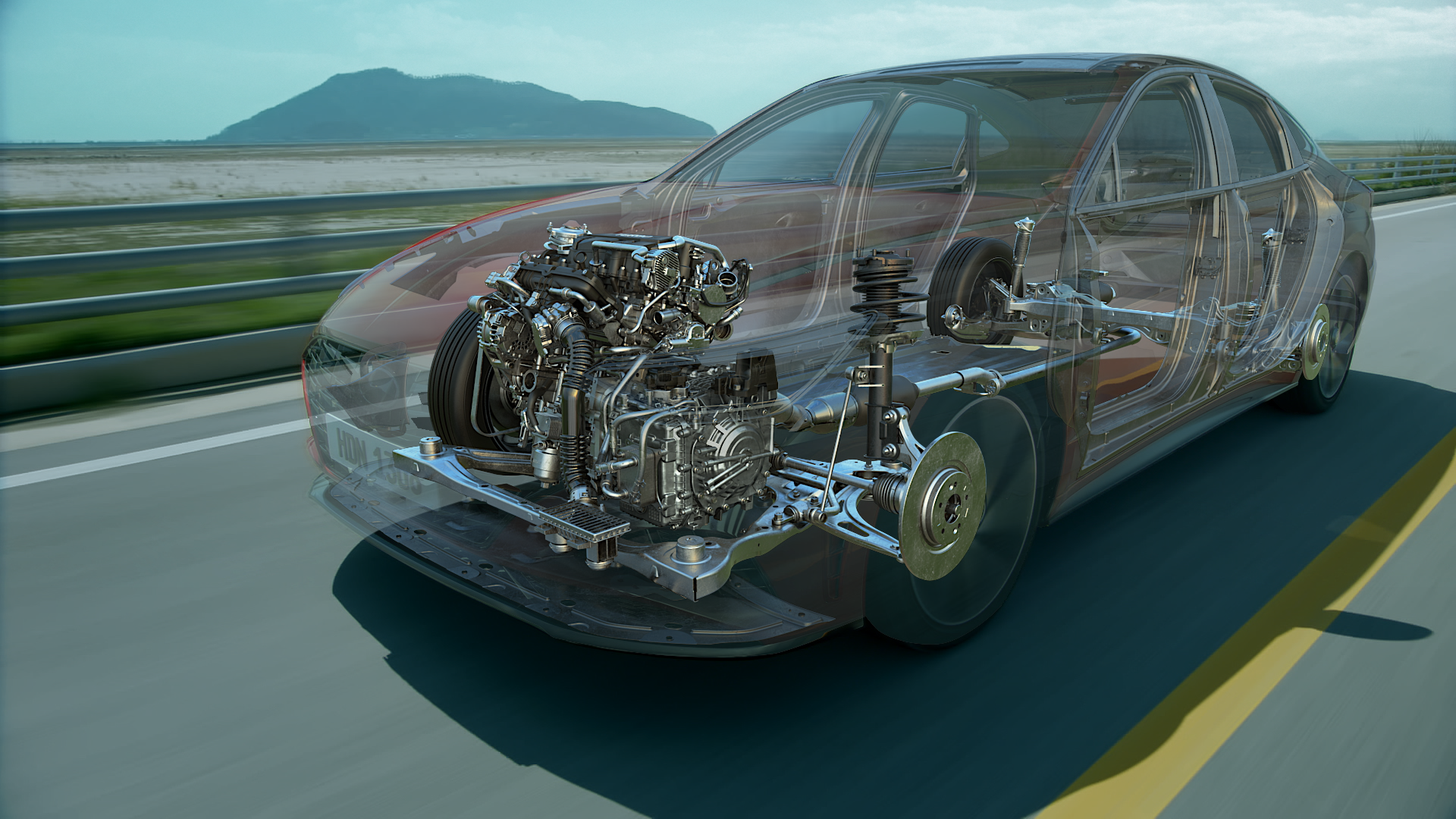


The engine consists of two main parts: the cylinder block - the body of the main moving parts of the engine and the removable top cover - the cylinder head. These two parts differ in many other details, the harmonious operation of which ensures the purposeful operation of the engine.

The engine block is the main component of an engine. It contains several openings for cylinders, coolant, and oil, which flow through them to cool and lubricate the engine. The engine block also houses pistons, the crankshaft, the camshaft, and typically has four to twelve cylinders. It is within the engine block that the combustion of fuel takes place.
ENGINE BLOCK FASTENING PARTS
All other engine components are fastened to the engine block using bolts. These fastening parts secure various engine parts and ensure their proper alignment and functioning.

The cylinder head contains various components, including valve springs, valves, pistons, rocker arms, and camshafts, which control the channels allowing the intake air to enter the cylinders during the intake stroke. The cylinder head also has exhaust channels through which the exhaust gases are expelled during the exhaust stroke.
ADDITIONAL CYLINDER HEAD PARTS
The cylinder head is attached to the engine cylinders using bolts and sealed with a head gasket. This ensures proper connection and sealing between the cylinder head and the engine block.
CYLINDER HEAD COVER
The cylinder head cover of the engine houses the top components of the engine control block and the crankcase ventilation valves. The cylinder head cover also protects the engine from dirt or other foreign objects.
CRANKCASE VENTILATION
The crankcase ventilation system removes unwanted gases from the crankcase. The system typically consists of a tube, a one-way valve, and a vacuum source.
TIMING BELT
The timing belt controls the intake and exhaust valves, allowing the fuel and air mixture to enter the engine and the exhaust gases to be expelled.

The crankshaft is located in the lower part of the engine block. This mechanism is connected to the pistons through the connecting rods. The crankshaft converts the reciprocating motion of the engine pistons into rotary motion through the crankshaft journal. The operation of the water pump, oil pump, generator, and other mechanisms directly depends on the rotation of the crankshaft.
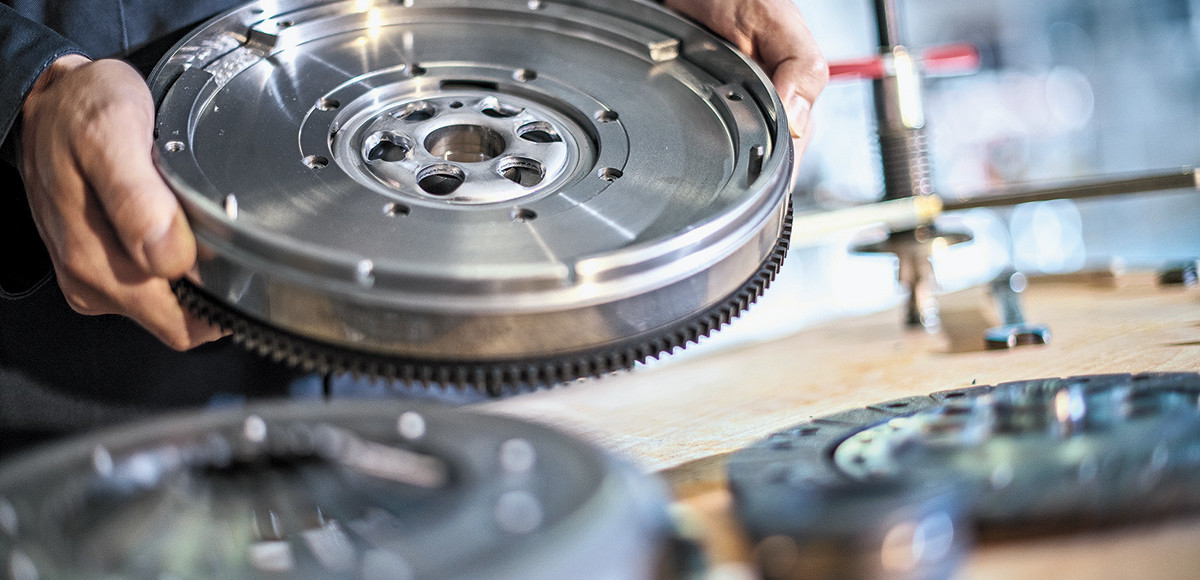

The flywheel is a round component of the distribution shaft. It is responsible for smoothing out the movement of the vehicle. The torque provided by the engine is not constant, so the flywheel maintains the torque when its value is high and releases it when its value is low.
LOWER DISTRIBUTION MECHANISM HOUSING
The distribution mechanism controls the timely intake of air into the cylinders and the removal of exhaust gases from them. It consists of valves with springs, a distribution shaft with lobes, and parts that transmit the shaft's motion to the valves.
DISTRIBUTION CHAIN - DISTRIBUTION MECHANISM CHAIN
The distribution mechanism chain transfers power from the crankshaft camshaft to the distribution shaft camshaft.
VALVE DISTRIBUTION MECHANISM
The distribution system includes intake and exhaust valves. Modern engines typically have one to three intake valves and one or two exhaust valves per cylinder.
Intake valves with springs regulate the supply of air into the cylinders from the intake system. Exhaust valves with springs regulate the removal of exhaust gases from the cylinders into the exhaust system.
LUBRICATION SYSTEM - OIL PUMP WITH CHAIN
The oil pump circulates oil. The pump is used for the transfer of fluids such as gear oil, transmission fluid, power steering fluid, hydraulic oil, and compressor oil.
OIL PAN | OIL FILTER | OIL LEVEL SENSOR
The oil pan is a metal container covering the bottom of the engine block. It serves as a reservoir for circulating engine oil.
The oil filter is used to remove debris, dirt, and metal fragments from the engine oil.
The oil level sensor is used to monitor the oil level. It constantly measures the engine oil level in both static and dynamic conditions.
COOLING SYSTEM - COOLANT PUMP / THERMOSTAT
The purpose of the cooling system is to maintain the proper engine temperature. It removes excess heat and protects the cylinder walls from overheating.
The coolant pump is driven by a belt from the crankshaft. By operating the pump impeller, it circulates the coolant from the pump.
The thermostat regulates the cooling of the car. It opens or closes valves that allow coolant to flow into the radiator.
TURBOCHARGER
A turbocharger is a device mounted on an engine to improve its performance and increase its efficiency. The turbocharger consists of two halves connected by a shaft. On one side, hot exhaust gases spin the turbine, which is connected to another turbine that draws in and compresses air into the engine. This compression provides the engine with additional power and efficiency by allowing more air to enter the combustion chamber, enabling more fuel to be injected and increasing power output.
OIL SUPPLY TO THE TURBOCHARGER
Oil ensures lubrication and proper functioning of the turbocharger bearings, transfers heat from the turbine to the compressor barrier, removes contaminants, and creates suitable conditions for the labyrinth seal ring. Oil is supplied under pressure to the bearing housing, then to the journal bearings and the thrust system.
TURBOCHARGER COOLING SYSTEM
The turbocharger must withstand high temperatures, which is why a turbine cooling system is installed. Its purpose is to reduce the intake air temperature to a level lower than the ambient temperature.
Some turbochargers are cooled by air and flowing oil, while others are cooled by water and oil. Accordingly, some have intermediate or intake air coolers that take hot compressed air from the turbine and cool it before reaching the engine, while others have a separate cooling water reservoir.
TURBOCHARGER HEAT SHIELD
The turbocharger heat shield is a device designed to maintain heat in the turbine housing. It helps increase the airflow speed and reduces turbine vibration.
INTAKE MANIFOLD
The intake manifold is an engine component that distributes the airflow among the cylinders. The intake air flows through the air filter, the intake port, then through the throttle valve into the intake manifold, and finally through the runners into the cylinders.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
The exhaust manifold is a device made of cast iron or stainless steel that collects the engine's exhaust gases from the cylinders and directs them into the exhaust pipe.
VACUUM PUMP WITH LINE
Vacuum pumps are used in vehicles where the intake manifold does not create the necessary vacuum, such as direct injection engines and turbocharged engines. The vacuum pump may also be used due to an increasing number of pneumatic systems.
The main function of the vacuum pump is to draw air from the brake booster reservoir, creating a vacuum that is used to operate the brakes.
ENGINE SOUND INSULATION
Engine insulation prevents the heat and noise generated by the engine from entering the car's cabin. Materials used for automotive sound insulation can be categorized as vibration-insulating, sound-insulating, or sound-absorbing. Typically, bitumen-polymeric or rubber-based sheets are used to reduce vibrations. Combined materials such as foils, foamed rubber, and layers of bitumen mastics are often used for sound insulation.
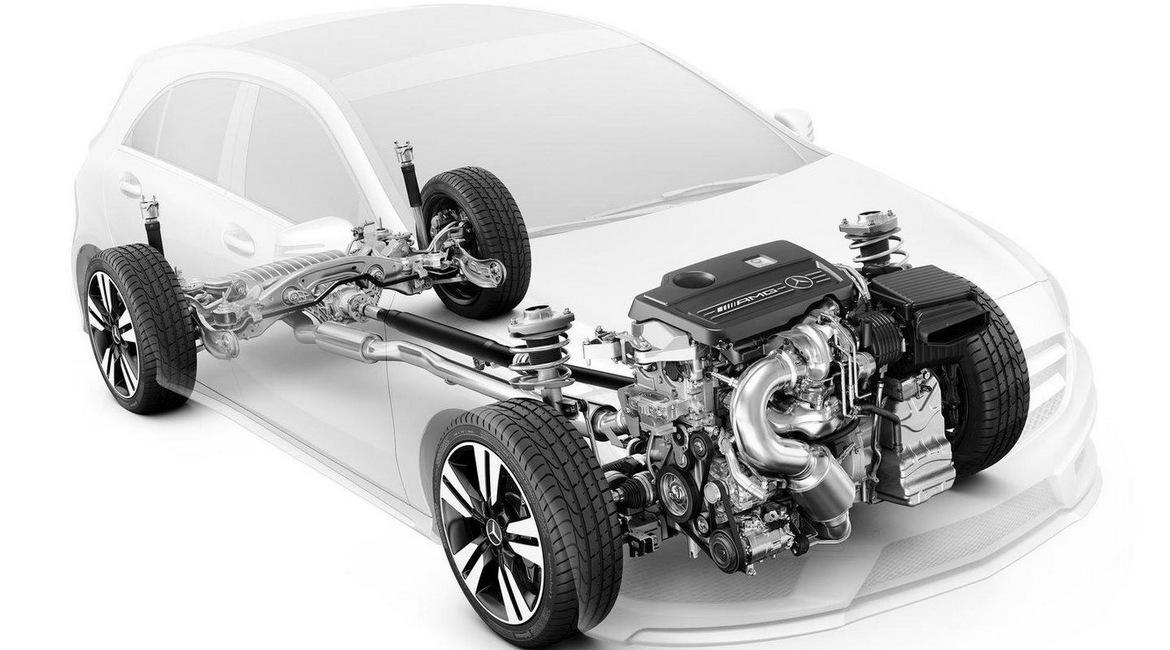

Whether it's an internal combustion engine, electric or hybrid, they all work on the same principle - they convert some form of energy into mechanical work that allows the car to move and drive.

Internal combustion engine is a heat engine. It converts the thermal energy generated during fuel combustion into mechanical work, namely torque. The explosive force of the air-fuel mixture in the engine rotates the pistons located in the cylinders, the pistons rotate the crankshaft, and due to its rotational force, the vehicle wheels turn.
Although internal combustion engines can be classified based on various criteria, such as the type of ignition fluid formation, the type of ignition of the mixture, the number and arrangement of cylinders, the sequence of the working cycle, the most clear and well-known classification of internal combustion engines is based on the type of fuel. According to this criterion, internal combustion engines are divided into gasoline engines and diesel engines.

The main difference between diesel and gasoline engines is the ignition system. Gasoline engines use spark ignition, where the fuel and air mixture is ignited by a spark. In these engines, the fuel is combined with air in the cylinder chambers and injected into the combustion chamber. The air-fuel mixture in the chamber is ignited by a spark from the spark plug, creating thermal energy that propels the vehicle.
Advantages of a gasoline engine:

Diesel engines operate on a compression ignition system. In these engines, fuel is injected into the combustion chamber and ignites due to the high temperature of the compressed air. The high air temperature is achieved through adiabatic compression, a process in which no heat exchange occurs between the system and the surroundings. In diesel engines, only air is compressed, not the fuel. When fuel is injected into the combustion chamber, diesel ignites spontaneously.
Advantages of a diesel engine:
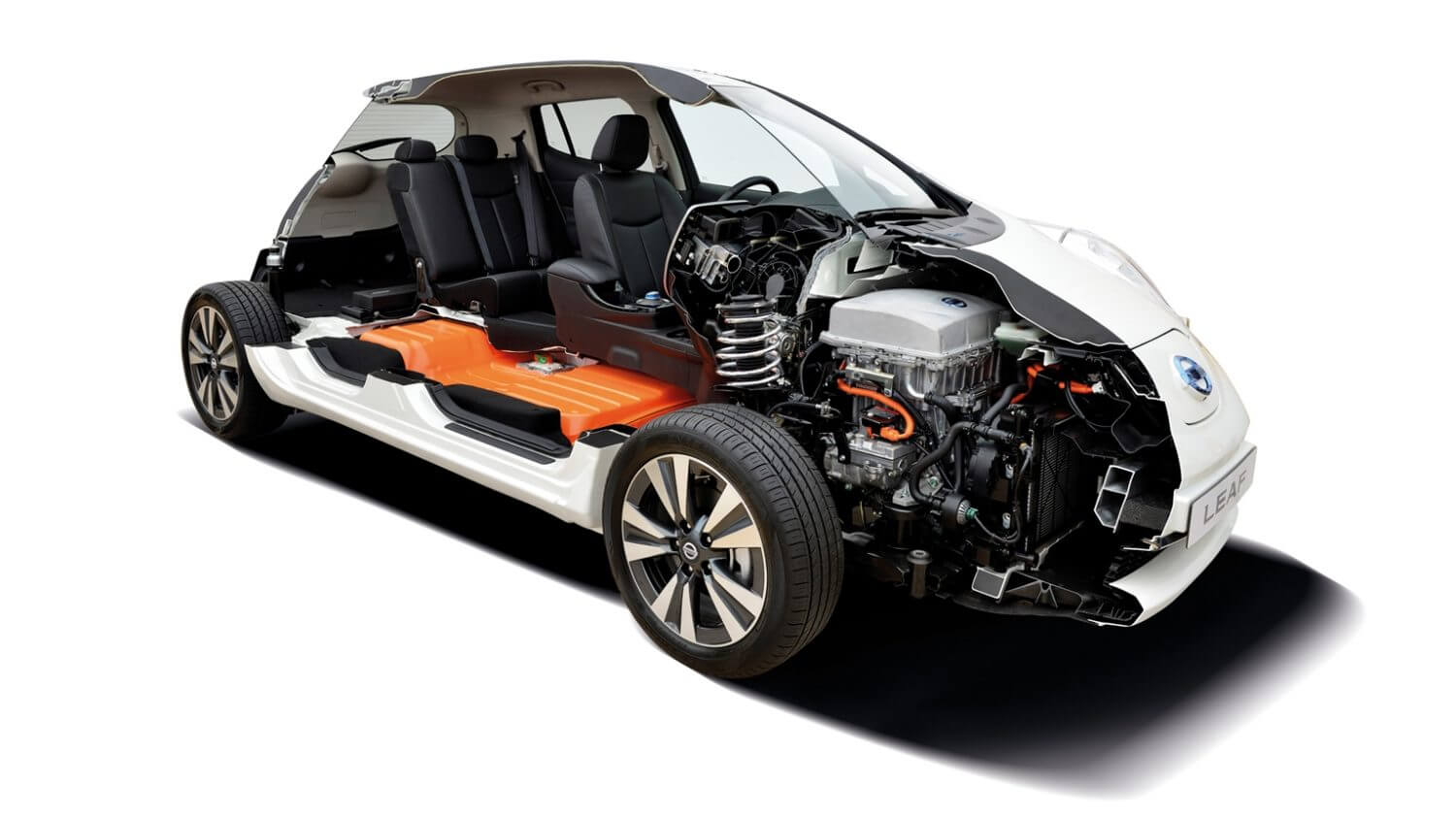

An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Through the interaction of the motor's magnetic field and electric current generated in the winding, a torque is produced, which helps propel vehicles.
Advantages of an electric motor:
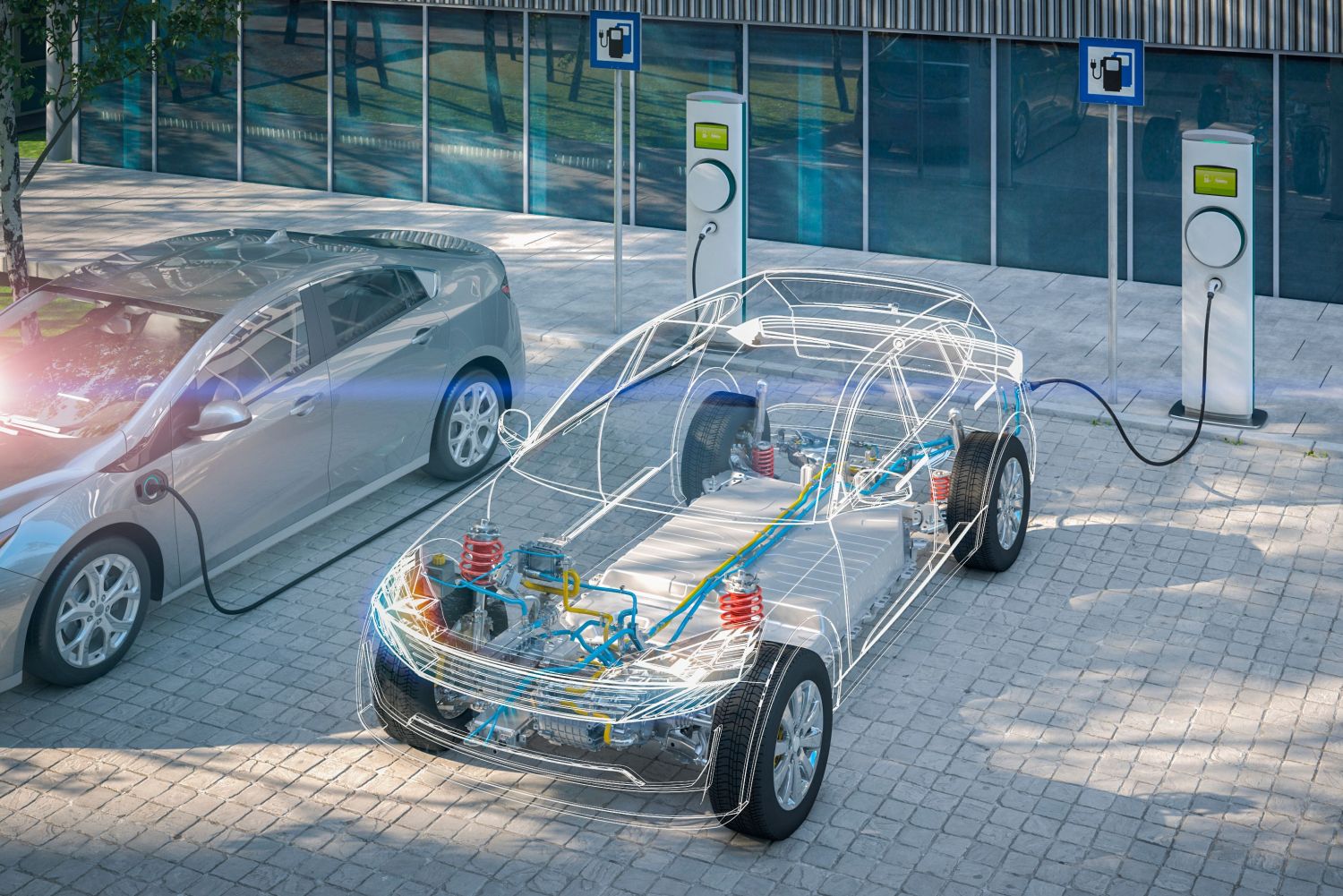

The operation of electrically driven vehicles varies. They can be classified as: plug-in electric vehicles, plug-in hybrid vehicles, and hybrid-electric vehicles.
Plug-in electric vehicles, or simply electric vehicles, are solely powered by electricity.
Plug-in hybrid vehicles are vehicles that can be powered by both electricity and fuel. These vehicles can use electricity and switch to fuel when the battery is depleted.
Hybrid-electric vehicles are primarily driven by fuel, but they also have an electric battery that can be recharged through regenerative braking. Drivers can switch between the fuel and electric motor by simply pressing a button.